Explore the data
Explore the data we have collected from around the world and learn how often psoriasis occurs in different groups of people.

An estimated 60 million people have psoriasis worldwide.
Only 19% of countries have epidemiological data on psoriasis.
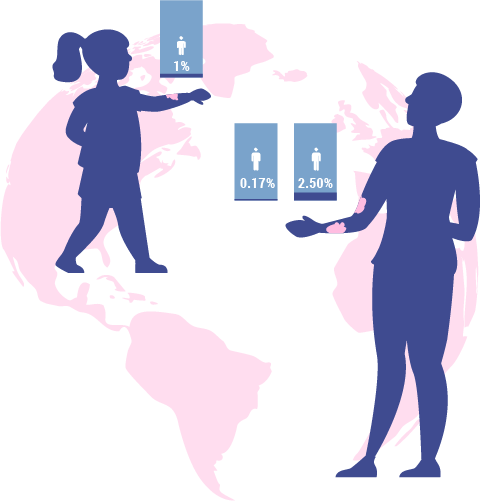
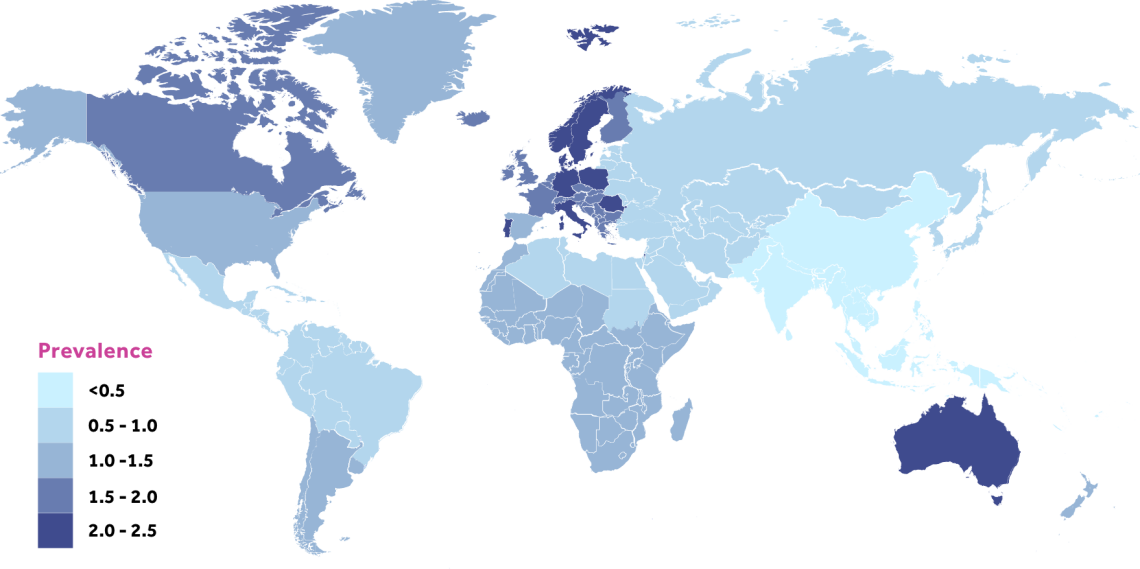
The prevalence of psoriasis in children is below 1% in every country. In adults, the prevalence of psoriasis varies betwen 0.17% in East Asia to 2.50% in Western Europe.
Psoriasis prevalence varies depending on geographic location.
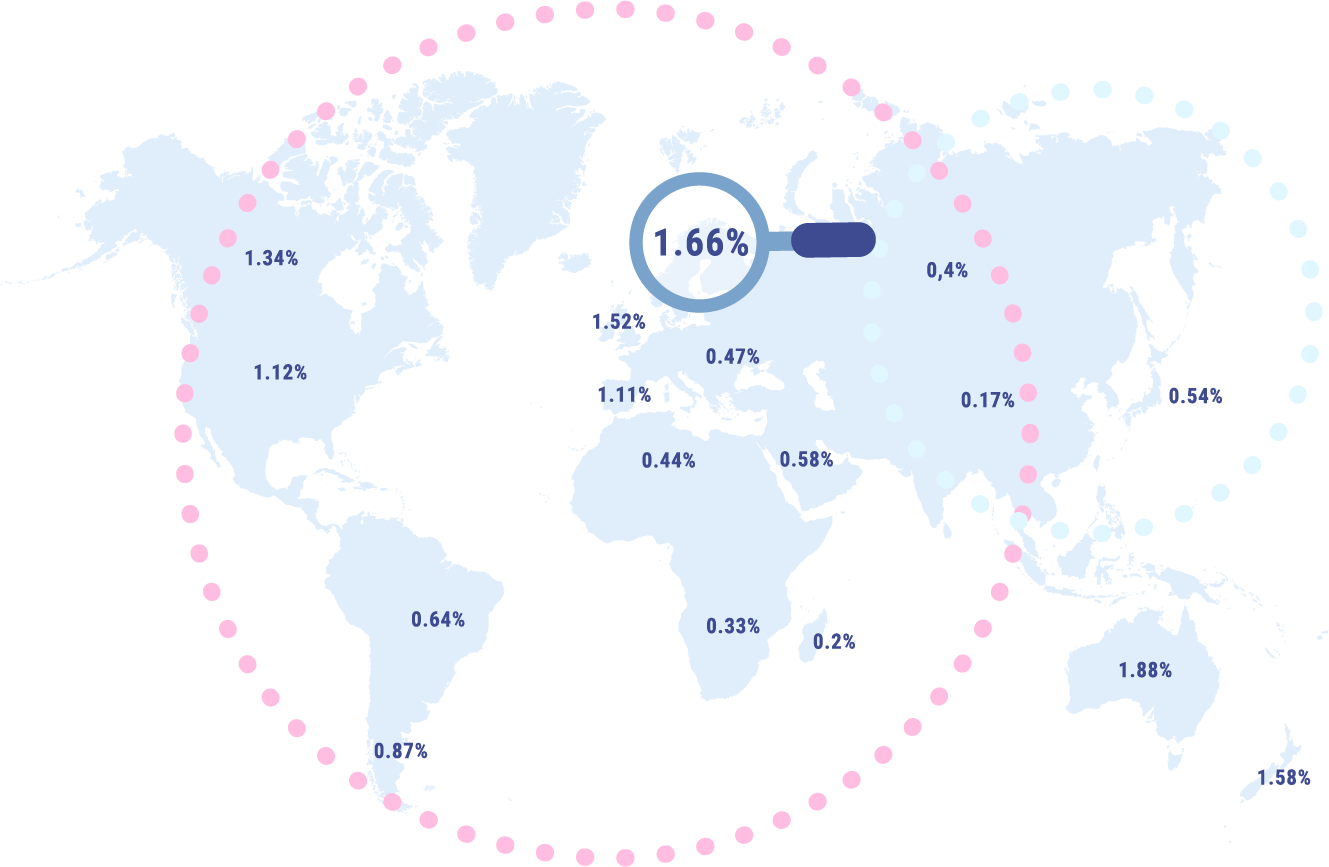
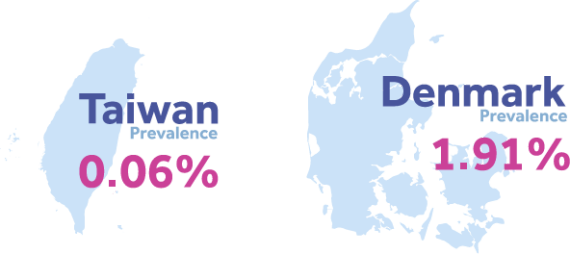
Our data indicates a prevalence estimate of 0.06% in Taiwan compared to a prevalence estimate of 1.91% in Denmark.
Studies worldwide suggested a stable or slightly decreasing trend in psoriasis incidence, while an increasing trend in psoriasis prevalence has been consistently reported.
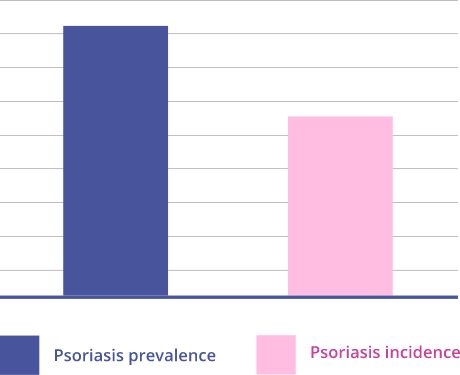

Further research is required to determine the reasons driving the increase in psoriasis prevalence over time.
Eighty one per cent of the countries of the world lack information on the epidemiology of psoriasis.

Considerable gaps still exist in the geographical areas reporting data on incidence and prevalence of psoriasis.
Research guide
INTERPRETATION OF THE ESTIMATES OF THE PREVALENCE OF PSORIASIS
HOW PREVALENCE ESTIMATES HAVE BEEN CALCULATED?
An extensive search of all available evidence was conducted and all the published articles on the prevalence of psoriasis were identified. All the information reported was assessed and used them to inform a statistical model. The statistical model generated a pooled estimate of the prevalence of psoriasis for each individual country where data were identified. Each prevalence measure is presented together with a range (uncertainty interval) which represents the uncertainty surrounding the estimate. Therefore, these values are not to be interpreted as exact measures, but only as measures which can vary within a certain range.
COUNTRIES WITH MISSING DATA
To be noted, many countries of the world do not provide information on the prevalence of psoriasis. For these countries, without high quality original data sources, estimates were generated by extrapolation, making using of the psoriasis prevalence estimate of the region the country was nested in, grouped according to the United Nations classification. Therefore, extrapolated estimated are less reliable, than for countries with original data sources and should be interpreted with caution. Please note, a publication will be available soon where all the countries with extrapolated estimates will be listed in a Table.
ADULTS
Refers to all adult population.
AGE-SPECIFIC RATE
A rate for a specified age group (adults or children), in which the numerator and denominator refers to the same age group.
AGE-STANDARDISATION
A statistical technique that facilitates comparison of prevalence rates either between populations or over time, adjusting for differences in the age structure of the general population in the countries or regions being compared.
CHILDREN
Refers to all children and adolescents individuals.
COUNTRY
Prevalence data are presented for 196 countries of the world *. Countries are nested into regions which are nested into super-regions.
DIAGNOSIS
The process of identifying a disease by its signs and symptoms. The diagnosis of psoriasis can be made either by a general practitioner/ physician or by a dermatologist.
INCIDENCE
The number of new cases arising in a given period in a specified population. This information can be expressed as an absolute number of cases per year or as a rate per 100,000 persons per year.
META-ANALYSIS
A statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple studies addressing the same question with the aim of deriving a pooled estimate closest to the unknown common truth.
OVERALL POPULATION
Refers to all individuals of any age, therefore children and adults combined.
PREVALENCE
The existing number of persons in a defined population who have been diagnosed with psoriasis. It is usually expressed as a proportion and can assume different definitions according to how it is measured. Therefore, it can be classified into: point, period and lifetime prevalence. Point prevalence: when the number of cases refers to a specific time point (e.g. a year). Period prevalence: when the number of cases refers to a time-window (e.g. between 2000 and 2010). Lifetime prevalence: when it refers to the entire previous life of an individual (e.g. “Have you ever been diagnosed with psoriasis?”).
REGION
Prevalence data are presented for 21 regions of the world (which contain 196 countries) *. Regions are nested into super-regions.
SUPER-REGION
Prevalence data are presented for 7 super-regions of the world (which contain 21 regions in which are nested 196 countries) *.
UNCERTAINTY INTERVALS/CREDIBLE INTERVALS
Uncertainty intervals have been produced by the statistical models to quantify the uncertainty around prevalence estimates. These intervals thus reflect the uncertainty levels around the psoriasis prevalence estimates.
*according to the definition of the United Nation - https://population.un.org
Research guide


